It is customary to call human parasites all organisms that live at their expense. These are bacteria, fungi, worms. Human parasites are divided into internal and external. The most unpleasant and most destructive to the body are helminths - a huge number of parasitic worms.
Parasites and the human body
The creatures parasitizing on the human body can be external or internal. External include:
- Mosquitoes.
- Leech.
- Lice.
- Microorganisms that cause scabies.
But there are many more creatures that prefer to settle in the body. These include:
- Bacteria.
- The easiest.
- Helminths.
- Mushroom.
The parasite's external and internal organization is among the simplest. Due to the fact that they do not have to evolve to survive, their organization is greatly simplified.
There are many creatures who prefer to settle in the body. For example, it can be bacteria.
They cannot survive without a host organism as they are unable to obtain their own food. However, they all reproduce very quickly, almost without exception, especially under suitable conditions. Where they are not driven immediately.
They differ geographically. Some can be found everywhere, no climate is an obstacle for them. Others live exclusively in tropical countries, but on the human body they can easily be brought to others. They also settle in different places in the body.
The luminal parasites are satisfied with the hollow parts of the body, and the tissue parasites live in the tissue.
The development cycles of parasites, mainly helminths, are also different. Some first develop in the ground (biohelminths) and then move to a living being. Others must first develop in the body of another living being, but not a person. Still others in an already adult state can be transmitted to another or re-infect themselves.
It is a mistake to assume that infection can only come from dirty hands. The eggs of some helminths are viable outside the nutrient medium for six months and adhere well to animal hair. Eggs survive even in dangerous environments - if you cook meat or fish incorrectly, a whole brood of worms can colonize you.

It is worth cooking the meat incorrectly, as a whole brood of worms can settle in you.
Human endoparasites
Parasites are divided into endoparasites and ectoparasites. Endoparasites - those who live inside, ecto - outside. Endoparasites can settle in almost all internal organs and tissues in the body. They are divided according to their localization. Endoparasites are:
- Endoparasites of internal organs that connect with the external environment.
They settle precisely in the organs that are connected to the external environment, not the other way round: the parasitic organism does not choose to "breathe". These organs include the intestines, lungs and the human urinary reproductive system. These are amoebas, Worms and parasitic flagellates.
- Blood parasites.
They live in human blood. They can live in plasma, white blood cells, and red blood cells. These are trypanosomes, microfilariae or hemosporidia.
- Tissue endoparasites.
These endoparasites that choose the tissues of the body as their place of residence. Muscle tissue, brain, cartilage, connective tissue. Tissue endoparasitis can even settle in nerve fibers. These are the Finnish tapeworms, trypanosomes, myxosporidia, trichinae and others.
Endoparasites can choose the brain as their place of residence.
The definition of the type of parasite by the place of its localization is rather arbitrary. Many species can migrate through various internal organs and regularly migrate through the host's body. The reproductive process can take place in one place and organisms exist directly and feed on another. The place where the parasitic creature settles and is considered the place of its conditional localization.
Despite the simplification of many parasite systems, their life cycle is quite complex.
Some species have to change several hosts in the course of their life, which can belong to different biological species. Others can only survive within one species, but may require intermediate hosts. They multiply in one person and develop and mature in another. With such a complex life cycle, their sexual functions are significantly increased. In order to survive in the body, parasites have to multiply quickly and vigorously.
Helminths
There are three main types of worms, also called worms. The:
- Nematodes, they are roundworms.
- Cestodes, ribbon-shaped endoparasites.
- Trematodes, also known as leeches.

Geohelminths begin their existence in the soil of the earth.
Furthermore, they can be divided according to the length of the life cycle and the number of places they pass along the way. There are also three types:
Geohelminths
"Geo" is the earth. These worms begin their existence in the soil of the earth, only after the stage of maturation can they infect a person. They do not need intermediate hosts, eggs end up in the soil along with human feces. Up to the larval stage, they only develop in the warm season.
Such worms include roundworms, gut eels, necators and whipworms.
The larvae of these parasites can enter the human body through unwashed vegetables or direct contact with the soil.
Biohelminths
These are parasitic worms, the life stages of which go through several hosts. Depending on the worm type, there may be two or more intermediate hosts. Some parasites only change one person. Others use the organisms of other biological beings for development before they finally enter the human body.

You can get infected from pets or contact with other people, as well as from eating semi-raw meat. Biohelminths include beef tapeworms, echinococcus, broadband worms, trichinae and others.
Contagious worms
These worms do not need soil or intermediate hosts. They go through all phases of their life cycle in an organism, very conveniently located. The larvae are excreted directly from the human body, when they come into contact with household surfaces and other people, they spread freely.
Helminths can live in various organs and systems in the human body and regularly migrate from one part of the body to another.
The list of diseases caused by helminths is very extensive. It can be determined which parasites live in the body and what treatment can be started only after passing all the tests necessary to determine the type of tests.
Round worms
The most widespread in the human environment are roundworms, also called nematodes. In total there are more than 24, 000 species of nematodes worldwide.

The most common human nematodes are roundworms.
They are called round because of their shape, which can be seen in a cross-section. The most common human nematodes:
- Ascaris.
- Pinworms.
- Trichina.
- Vlasoglava.
Helminth infestation known as ascariasis begins with direct contact with worm-infested soil or with the consumption of unwashed fruit and vegetables. Parasites begin to develop in the intestines, and then enter the human circulatory system, from where they go to various internal organs and enter the oral cavity. Without realizing it, a person swallows an already adult parasite again. They feed on the remains of undigested food. Ascaris waste products are extremely toxic. There is no vaccine against ascariasis, infection can only be prevented by following the rules of personal hygiene.
A pinworm infection is known as enterobiasis. These are small worms (5-10 mm) that attach themselves to the walls of the intestines. They feed on blood and intestinal contents. They lay their eggs under the skin and rise from the anus while the owner sleeps. Due to the itching, a person scratches the anal area, the larvae get under the skin and on the hands, and can easily be transmitted to other people in the house or public places. There are no painful symptoms in enterobiasis, it is extremely problematic to identify pinworm infection in the early stages.
Trichinella, they are also Trichina, are roundworms that choose an animal or person as their owner.
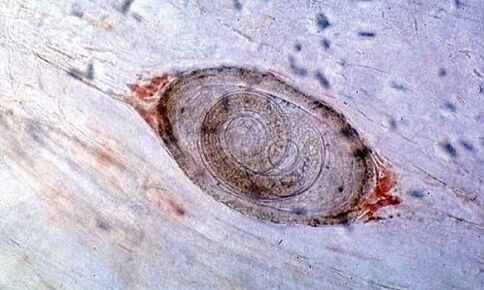
Trichinella is a parasitic worm that infects the human body and causes the dangerous helminth disease trichinosis.
They begin to develop in the area of the striated muscles in the body and then are redirected to the small intestine. In advanced cases of infection, there can be around 15, 000 Trichina eggs per kilogram of muscle tissue. These parasites can cause a deadly disease named for their source - trichinosis.
The whipworms are so named because of their appearance. The front part of her small body is thread-shaped, with an esophagus in it.
The rear part is wider, the rest of the parasite's internal organs are located in it. The whipworm can be up to 50 mm long. It feeds on blood and tissue fluid. Trichocephalosis causes the disease.
Tapeworms
There are around 3, 500 known tapeworm species, also called cestodes, worldwide. These flatworms have no digestive systems at all, and the diseases they cause are known as cestodoses.
The most common cestodoses:
Cysticercosis
The disease is caused by pork tapeworm larvae that get inside through contaminated food from dirty hands.
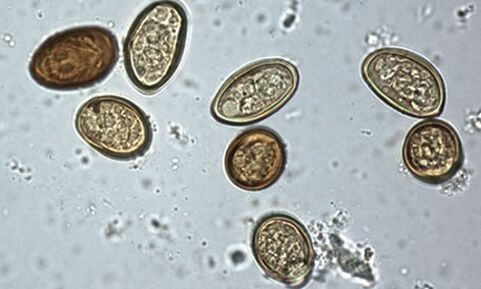
The disease affects the skin, bones, internal organs, brain, and spinal cord. Most often, parasites are sent to the brain (in 60% of cases of infection). Diagnosis is based on the appearance of rounded formations on the skin. The disease is treated; if the central nervous system is infected, the prognosis may be poor.
Echinococcosis
It is localized in the liver, lungs, and many other internal organs. Echinococcus larvae cause the disease. They can develop in a person over several years.
Infection occurs through contact with animals, picking berries and fruits, drinking contaminated water.
The course of the disease is not too noticeable, it can develop over the years and is only discovered by chance.
Alveococcosis
Alveococcosis is caused by the larvae of alveococcal worms. The disease is similar to echinococcosis, but it is more serious. Affects the lungs and kidneys. Without treatment, the disease is very likely to be fatal due to the development of liver failure.
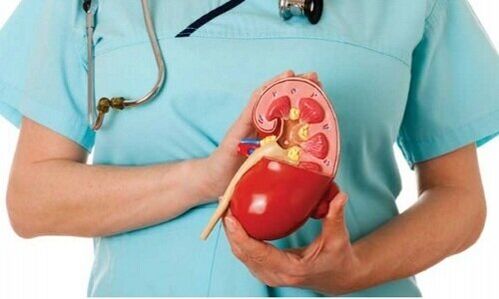
Alveococcosis most commonly affects the kidneys.
Teniarinhoz
Teniarinhoz is caused by a beef tapeworm. It parasitizes tapeworms in the area of the human small intestine and develops over a period of 2. 5 to 4 months. The prognosis for treatment is often favorable. Parasites can invade a person with infected raw or under-thermally processed meat.
Tapeworms are very productive. They have the least remaining sensitivity and no digestive system at all. Such parasites cannot develop without a host.
Fluke worms
Leeches are leeches. These are flat worms, the body shape of which resembles an elongated leaf on a tree.
Some types of trematodes can be up to five feet tall.
And they most often end up in the human body through fish or other seafood. About 7, 200 kinds of accidents are known, 40 of which inhabit humans and cause trematodes, a serious disease caused by infection.
The most common leeches:
Liver fluke
Widespread worldwide, can exist in animals and humans. The biological life cycle is complex, the parasite changes host.
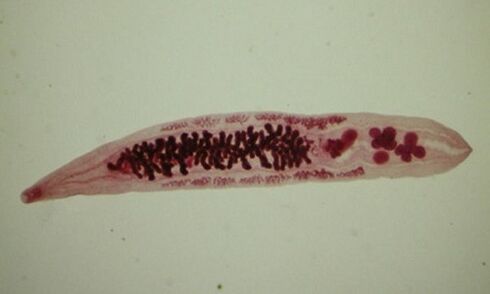
The most common coincidence is the liver fluke.
Schistosoma
Schistosome larvae can penetrate the skin or mucous membranes. The life cycle is complex, they feed on blood. A female can produce around 3000 eggs per day, the fertility of these parasitic worms is very high.
Other liver fluke
They cause opisthorchiasis, a helminth disease that mainly spreads to the liver. They have a toxic effect on the human body.
The digestive system of random worms, and with it the reproductive and excretory systems, is well developed.
The rest of the systems are performing poorly. Trematodes feed on blood, epithelial cells of the skin and intestinal contents. They can live almost anywhere: from the liver to the conjunctival sacs of the eyes.
Other types of endoparasites
The rest of the internal parasites are made up of a huge number of bacteria that cause dangerous diseases, and with them the simplest of microorganisms. The fungus that spreads in the human body also belongs to the segment of endoparasites.
Many beneficial and harmful microorganisms live in the human body. Some of them cause quite dangerous diseases that can lead to death. It is not always possible to immediately identify the presence of parasitic beings within yourself, but an early diagnosis of infection offers a better chance of a complete cure. If an invasion is suspected, it is recommended to undergo a full medical examination immediately.





































